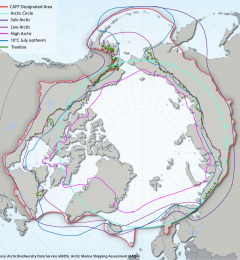
Data
Comprehensive biodiversity data can inform decision- and policy-making. While many such data already exist, the challenge lies in finding, accessing, and making sense of existing but dispersed data. Data are not always encoded in accordance with international data standards or best practices, and often lack the necessary contextual metadata required to correctly apply and interpret it.
Accessing Arctic biodiversity data from a range of sources and in variable formats can require a lot of effort from users to gather and assemble information.
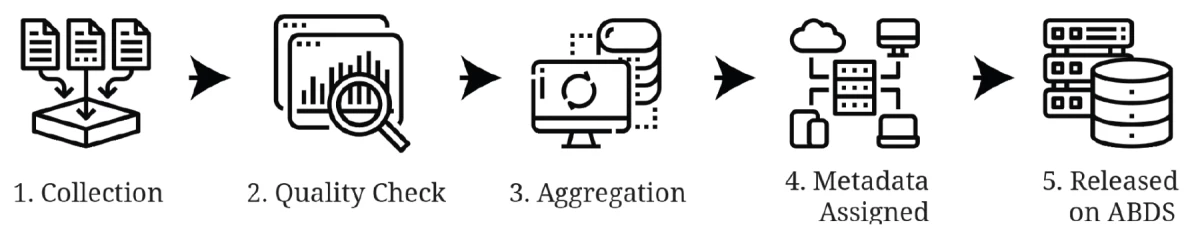
In response, the Conservation of Arctic Flora and Fauna (CAFF) initiated the development of the Arctic Biodiversity Data Service (ABDS) to serve as the data management system for biodiversity data generated via its monitoring and assessment activities. Each time a new report or product is released by CAFF, the datasets involved are archived and made accessible via the ABDS.
CAFF works with a range of partners including relevant national and international organisations to further develop cooperation, access to and management of biodiversity data. Key partners include the Arctic Spatial Data Infrastructure (Arctic SDI), Global Biodiversity Information Facility (GBIF), Ocean Biogeographic Information System (OBIS), Group on Earth Observations Biodiversity Observation Network (GEOBON), International Network for Terrestrial Research and Monitoring in the Arctic (INTERACT), Protection of the Arctic Marine Environment (PAME) Arctic Council Working Group and NatureServe.
 Arctic Council Working Group
Arctic Council Working Group