Icing events
E.g., loss of September sea-ice extent over five years exceeding 0.5 million km2.
The threshold is the freezing temperature (0C), the exceedance of which, on shorter timescales, and during winter precipitation events can result in freezing rain or rain-on-snow events.
Permafrost thaw has a clearly defined threshold (0C) but is largely dependent on the underlying (slow-onset) change in climate rather than short-duration warm events or single snowfall events.
Subsidence of the ground surface and the formation of uneven topography known as thermokarst, have implications for ecosystems, landscape stability, and infrastructure performance.
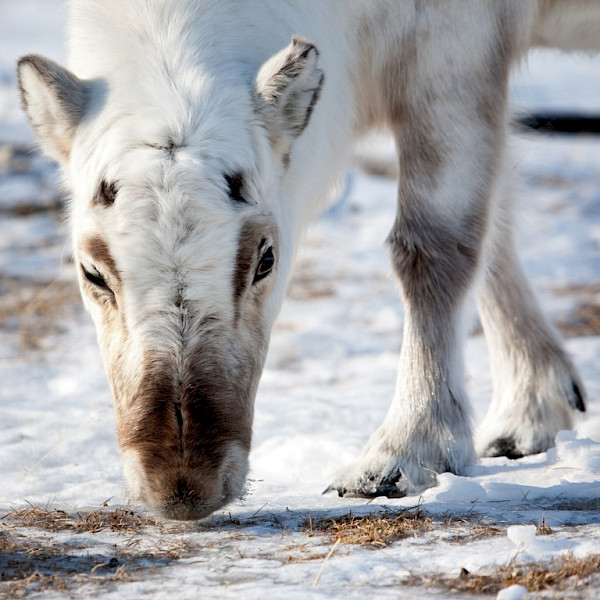

Photo: Tyler Olson/Shutterstock.com
| Description of extreme event | Detecting and monitoring the extreme event itself | Monitoring ecosystem impacts of the extreme event | ||||||||||
| Name | Description | Expected temporal scale of extreme event itself | Expected spatial scale of extreme event itself | Types of impact (and relevant cascading effects) | Definition of extreme event (see also Definition-sheet) | Variable to detect extreme event | Method to monitor (risk of) extreme event itself (if different from detection method) | Suggested background data needed to assess impact on ecosystem/biodiversity (if any)* | Suggested method to monitor impacts of extreme event (if different from or background data are missing) | Expected temporal scale of impact | Priority FECs to monitor | Reference/Links |
| Icing | Rain on freezing surfaces resuting in a layer of ice | Brief (< month) | Large (region/ > 10 km2) | Affect food availability. Affect reproduction and population size. Changes in herbivore population may affect predator populations and plant community composition | Formation of ice layer in vegetation or on snow > 10 mm | Observations of precipitation type and temperature | Snow structure measurements | Diversity, abundance, composition, productivity, phenology, spatial structure, ecosystem functions and processes, phenology, demographics, temporal cycles and health for flora and fauna | Monitor in affected and comparable reference area | < 5 years |
|
|
| ROS (rain -on-snow) | Rain on snow resuting in a layer of ice on top of the snow layer | Short (< day) | Large (region/ > 10 km2) | Impact ability of herbivores to reach food source under snow. Affect reproduction and population size. Changes in herbivore population may affect predator populations and plant community composition | Defined as a minimum of 3 mm of rain falling on a minimum of 5 mm of snow water equivalent. Freezing temperature (0C) | Preferredably dayly measurements of (type of) precipitation and snow layer thickness and temperature | Diversity, abundance, composition, productivity, phenology, spatial structure, ecosystem functions and processes, phenology, demographics, temporal cycles and health for flora and fauna | Monitor in affected and comparable reference area | < 1 year |
|
||
| De-icing of permanently frozen lakes | Melting of icelayer on hitherto permanently frozen lake surface, causing major shifts in lake ecosystem composition and processes. | Long (>years) | Small scale (Local,< 1 km2) | Impact lake physical properties, productivity, species composition and dispersal, | Loss of permanent ice cover on lake. | Observation of dissappeared icecover (partly or fully) | ||||||
 Arctic Council Working Group
Arctic Council Working Group