Events of extreme character
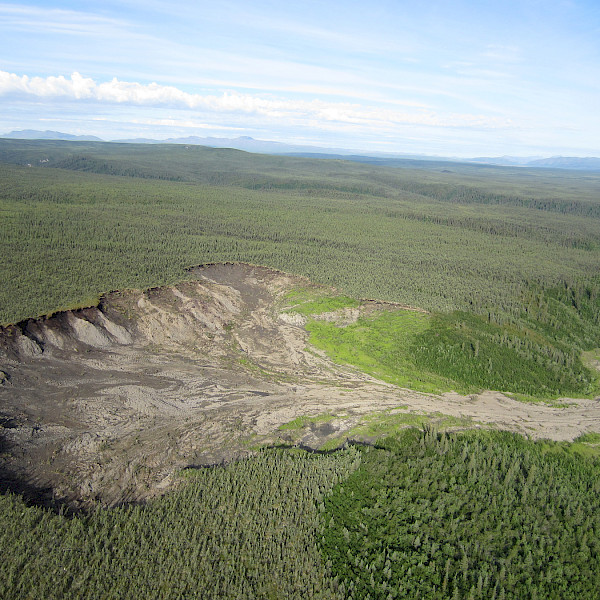

Permafrost slump in northern Canada.
Photographer: Jen Lento
Photographer: Jen Lento
Attention: Click at the table and use the arrow keys on the keyboard to move the table to right or left!
Download this table as CSV
| Description of extreme event | Detecting and monitoring the extreme event itself | Monitoring ecosystem impacts of the extreme event | ||||||||||
| Name | Description | Expected temporal scale of extreme event itself | Expected spatial scale of extreme event itself | Types of impact (and relevant cascading effects) | Definition of extreme event (see also Definition-sheet) | Variable to detect extreme event | Method to monitor (risk of) extreme event itself (if different from detection method) | Suggested background data needed to assess impact on ecosystem/biodiversity (if any)* | Suggested method to monitor impacts of extreme event (if different from or background data are missing) | Expected temporal scale of impact | Priority FECs to monitor | Reference/Links |
| GLOF (glacier-lake-outburst-flood) | Drainage of ice-dammed lakes or glacial outburst floods, occurs when a moraine is breached or an ice-dam fails | Short (< day) | Medium (Several catchments/ < 10 km2) | Impact on terrain, land organisms, their productivity, biodiversity and habitat composition by loss of substratum, flush and drowning | Flooding from outburst of a glacier lake | Air temperature measurements, satelite observations on glacier retreat and glacier lake size or water level measurements. Observation of outburst flood | Remote sensing or field measurements of affected area (size of area) | Diversity, abundance, composition, productivity, phenology, spatial structure, ecosystem functions and processes, phenology, demographics, temporal cycles and health for flora and fauna | Monitor in affected and comparable reference area | >5 years | ||
| Landslides | Collapse of a mass of earth or rock from a mountain or cliff | Short (< day) | Medium (Several catchments/ < 10 km2) | Plant species composition, potential long-term vegetation shifts with climate change | Rapid downward movement of soil/gravel/rocks down a sloped section of land under the influence of gravity | Annual remote sensing or ad hoc field observation of landslide prone areas | Remote sensing or field measurements of affected area (size of area). Drone identification of matter movement compared to baseline | Diversity, abundance, composition, productivity, phenology, spatial structure, ecosystem functions and processes, phenology, demographics, temporal cycles and health for flora and fauna | Monitor in affected and comparable reference area | >5 years | ||
| Permafrost thaw and thermokarsts | Melting of permafrost, subsidence of the ground surface and to the formation of uneven topography | Long (>years) | Small scale (Local,< 1 km2) | Emission of methane. Thermokarsts having implications for ecosystems, landscape stability, and infrastructure performance | Permafrost thaw has a clearly defined threshold (0C) | Soil temperature and location depth of permafrost | Diversity, abundance, composition, productivity, phenology, spatial structure, ecosystem functions and processes, phenology, demographics, temporal cycles and health for flora and fauna | Monitor in affected and comparable reference area | >5 years | |||
| Fire | Vegetation or underlying turf and peat has caught fire | Brief (< month) | Medium (Several catchments/ < 10 km2) | Burn down of vegetation, and loss of fauna from fire and burn down of habitat, loss of feed | Flames (open fire) or flameless combustion/smoulder from smoke or heat of vegetation or turf and peat | Alarm, remote sensing or ad hoc field observations of fire or smoke | Remote sensing or field mesaurements of affected area (size of area) | Diversity, abundance, composition, productivity, phenology, spatial structure, ecosystem functions and processes, phenology, demographics, temporal cycles and health for flora and fauna | Monitor in affected and comparable reference area | >5 years | ||
| Browning | The vegetaion cover turning brown due to die-off of vegetation | Long (>years) | Large (region/ > 10 km2) | Acute and extensive loss of plant biomass at landscape and greater scales, thus large-scale vegetation damage, habitat and food loss | Browning is a systematic decrease in vegetation growth or the death of vegetation that results in a negative trend in NDVI or productivity | Is observed using the same tools and methods used to identify greening | Diversity, abundance, composition, productivity, phenology, spatial structure, ecosystem functions and processes, phenology, demographics, temporal cycles and health for flora and fauna | Monitor in affected and comparable reference area | >5 years | |||
| Non-native invasive species | Introduction of a non-native species that becomes invasive, i.e., inhabits habitats otherwise inhabited by native species and out-competes them | Long (>years) | Large (region/ > 10 km2) | May out-compete native species and thus change habitats incl. loss of species, loss of food and change in prey/predator relationsships | Non-native (or alien) to the ecosystem and whose introduction causes or is likely to cause economic or environmental harm | Detection of introdution of potential invasive species | Systematic monitoring of flora and fauna | Diversity, abundance, composition, spatial structure, ecosystem functions and processes, phenology, demographics, temporal cycles and health and productivity for flora and insects | Monitor in affected and comparable reference area | < 5 years | ||
| Population outbreaks | An insect pest outbreak is a large and sporadic population of insect pests | Brief (< month) | Medium (Several catchments/ < 10 km2) | Larvae outbreaks may lead to canopy defoliation, decreased vegetation biomass, shifts in vegetation composition, decreased C uptake and cascading impacts through other food web compartments. Rodent outbreaks may lead to high pressure on vegetation | Pest population rises significantly above its general equilibrium level | Monitoring of fauna including focus on species known to have potential outbreaks | Systematic sampling and counting | Diversity, abundance, composition, spatial structure, ecosystem functions and processes, phenology, demographics, temporal cycles and health and productivity for flora and insects | Monitor in affected and comparable reference area | < 5 years |
|
|
| Decease outbreaks | Infectious disease agents in hosts of flora nad fauna | Brief (< month) | Medium (Several catchments/ < 10 km2) | Decease outbreaks may lead to loss of host and hence food availablity on higher trophic level | Detection of decease | Monitoring of fungi and microbiology including focus on pathogenic organisms | Systematic sampling and counting | Diversity, abundance, spatial structure, ecosystem functions and processes, phenology, demographics for decomposers | Monitor in affected and comparable reference area | < 5 years | ||
 Arctic Council Working Group
Arctic Council Working Group